LME quotations
London Metal Exchange (LME) is a key source of information for companies operating in the secondary raw materials sector, particularly those involved in the purchase and sale of scrap metal. LME quotations directly affect the prices of non-ferrous metals - such as copper, aluminium, lead, zinc or nickel - which dominate the scrap trade. Understanding how they work LME quotations and how to apply them in practice, is the foundation of effective and informed scrap business management.
Basic metal quotations on the LME
To use LME data, it is useful to know the basic types of quotation:
- LME Official Cash Buyer (L. Bid) - the price at which the LME would buy metal 'off the shelf' (spot). Most commonly used in the scrap industry.
- LME Official Cash Seller (C. Ask) - the price at which the LME would sell metal 'off the shelf'.
- LME Official Settlement Price - clearing price, used for futures pricing and hedging.
- LME Official 3-Month Buyer / Seller - price of contracts with delivery in 3 months (standard futures).
- LME Closing Prices - closing prices of the trading session.
- LME Settlement Prices - prices based on average end-of-day quotes; applied by the clearing house LME Clear.
- LME Average Prices - daily, weekly and monthly average prices, used in analyses and long-term contracts.
- LME Indicative / Off-Warrant Prices - Indicative prices for metals outside official LME warehouses.
In addition, the market uses terms such as:
- 3M (3-Month) - standard futures contract.
- Tomorrow-Next - price for next day delivery.
- Carry - price difference between contracts (e.g. spot vs 3M).
What is Contango and Backwardation?
Contango - a growing market
Contango occurs when futures prices are higher than the spot price. This is a typical situation with high stocks and low immediate demand.
Example of contango:
- Spot copper: USD 8 500/t
- 3M contract: USD 8 800/t
Causes of contango:
- Low current need for supply
- High storage costs
- High availability of raw material
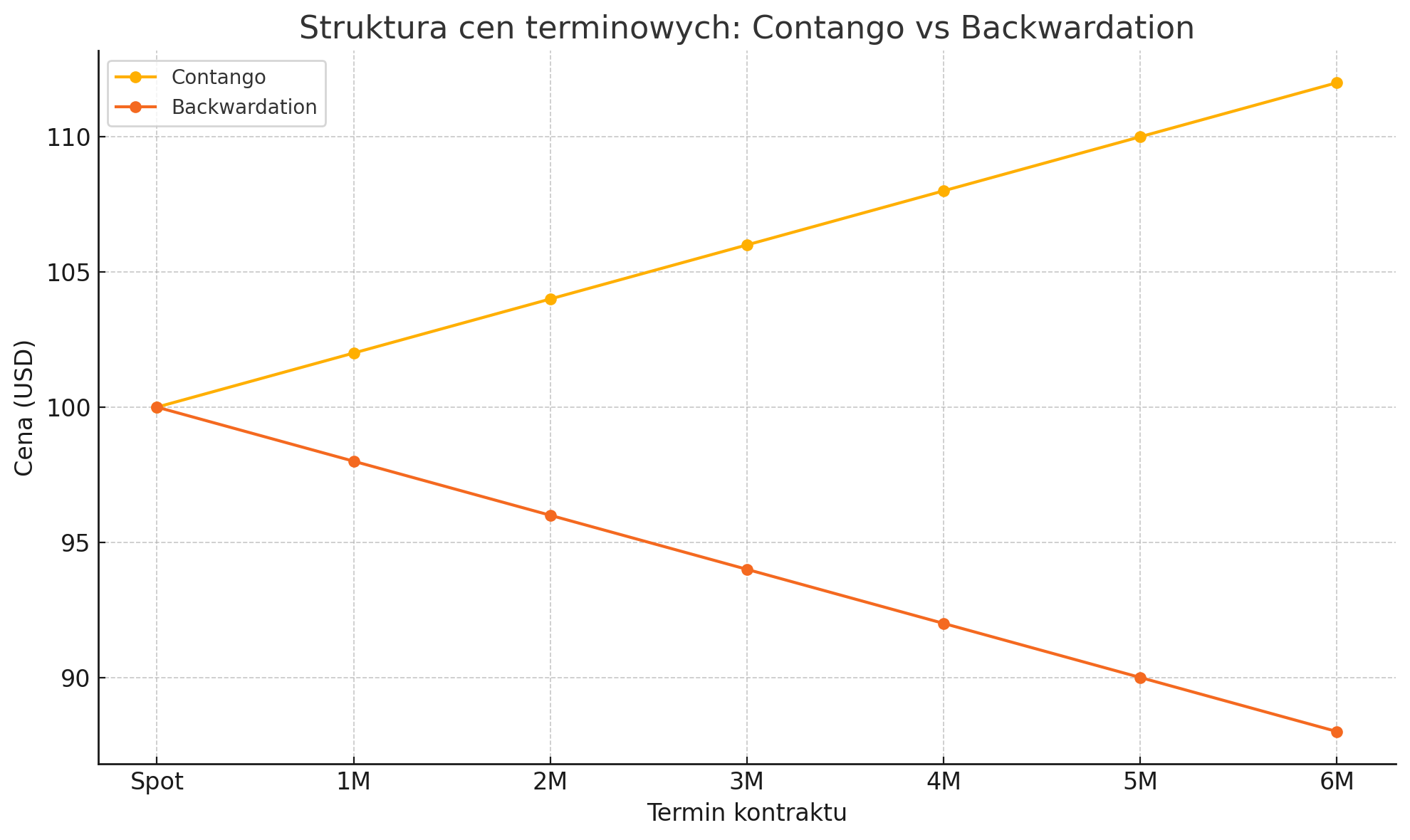
Backwardation - falling market
The reverse: futures contracts are cheaper than the spot price, suggesting supply tensions.
Example:
- Spot aluminium: USD 2 300/t
- 3M contract: USD 2 100/tonne
Causes of backwardation:
- Low stocks
- Urgent need for delivery
- High short-term demand
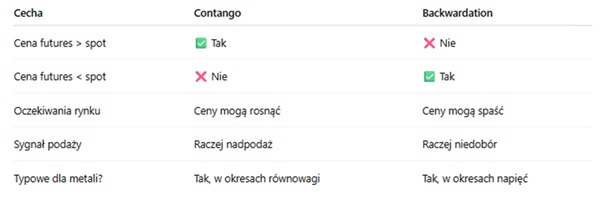
Comparison of contango and backwardation
LME and the scrap market
In practice, in the scrap metal industry, we most often rely on the LME Official Cash Buyer (L. Bid). It is a quotation that changes dynamically during the day, from 01:00-19:00 London time (02:00-20:00 Polish time in summer).
Another important reference is LME Official Prices, set between 11:40 and 13:10 (UK time), i.e. approximately 12:40-14:10 in Poland in winter / 13:40-15:10 in summer. Each metal is assigned its own 5-minute pricing window:
Metal | Hour (UK) | Hour (EN - summer) |
Aluminium | 11:55-12:00 | 12:55-13:00 |
Copper | 12:00-12:05 | 13:00-13:05 |
Zinc | 12:10-12:15 | 13:10-13:15 |
Lead | 12:15-12:20 | 13:15-13:20 |
Nickel | 12:25-12:30 | 13:25-13:30 |
Using LME it is worth remembering that the price of scrap does not always follow the LME directly.
What influences the price of scrap metal?
- Exchange rates (especially USD/PLN)
- Type and quality of scrap
- Terms of trade at steelworks and foundries (discounts, surcharges)
- Logistics costs and local demand/supply
It is often the case that LME rises in dollar terms, but scrap cheapens - e.g. because of the strengthening zloty or because LME prices are falling and scrap prices are not changing, as is sometimes the case with certain grades aluminium.
To conclude, it is worth adding that knowledge of LME quotations is a must today for any scrap company that wants to operate effectively in the market and control margins. However, it is equally important to understand that the LME is only a benchmark - the ultimate scrap price depends on a number of local and market factors.
Want to find out more, check out scrap metal buying RMC Poland.
RM 9.05.2025

